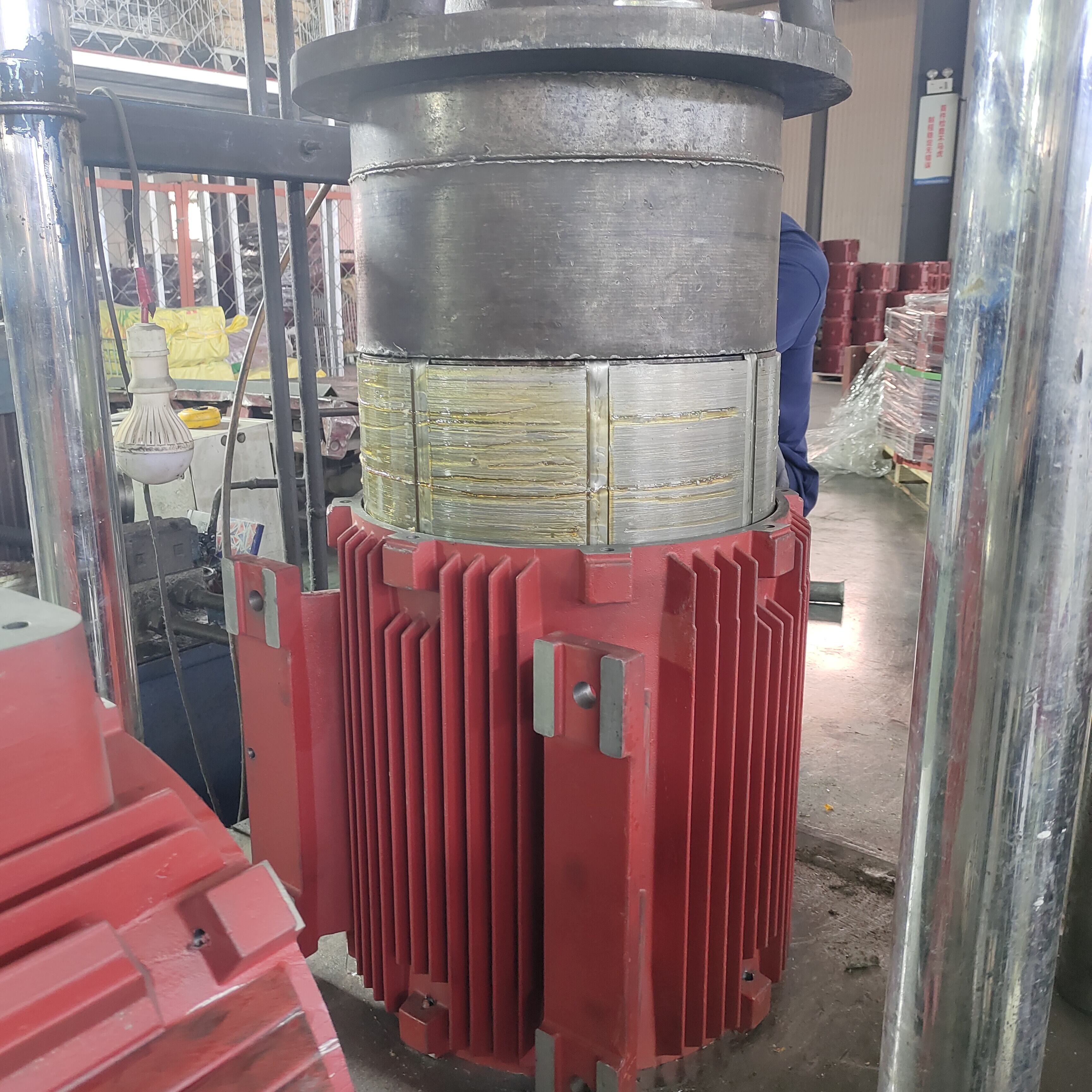
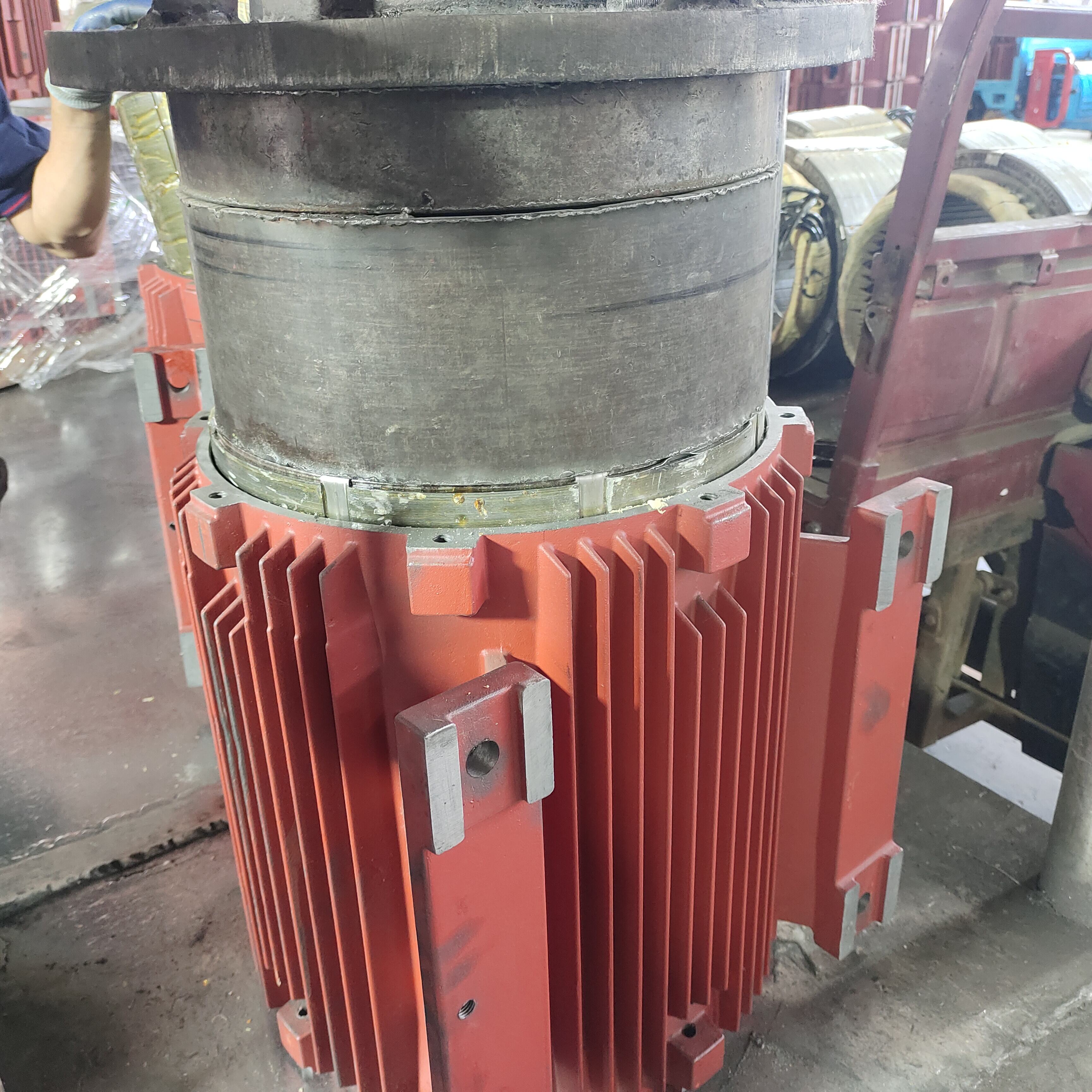
hot die casting
Hot die casting represents a revolutionary manufacturing process that transforms metal production through the application of controlled heat during the casting operation. This advanced technique involves injecting molten metal into precision-engineered steel dies while maintaining elevated temperatures throughout the entire production cycle. The hot die casting process operates by heating both the die and the molten metal to specific temperature ranges, typically between 200 to 400 degrees Celsius, depending on the metal alloy being processed. This temperature control creates optimal conditions for metal flow, reduces viscosity, and ensures complete die cavity filling. The main functions of hot die casting include producing complex geometrical components with exceptional dimensional accuracy, creating parts with superior surface finishes, and manufacturing components that require minimal post-processing operations. The technological features of this process encompass sophisticated temperature monitoring systems, automated injection mechanisms, and precision die design capabilities. Modern hot die casting equipment incorporates computer-controlled heating elements, advanced pressure regulation systems, and real-time temperature feedback loops that maintain consistent processing conditions. The process excels at producing thin-walled components, intricate internal passages, and parts with complex undercuts that would be challenging or impossible to achieve through conventional casting methods. Applications for hot die casting span numerous industries, including automotive manufacturing for engine components and transmission parts, aerospace sector for lightweight structural elements, electronics industry for heat sinks and housing components, medical device production for surgical instruments, and consumer goods manufacturing for decorative and functional hardware. The versatility of hot die casting makes it suitable for processing various metal alloys, including aluminum, magnesium, zinc, and specialized copper-based materials, each requiring specific temperature profiles and processing parameters to achieve optimal results.