warm drukgieting
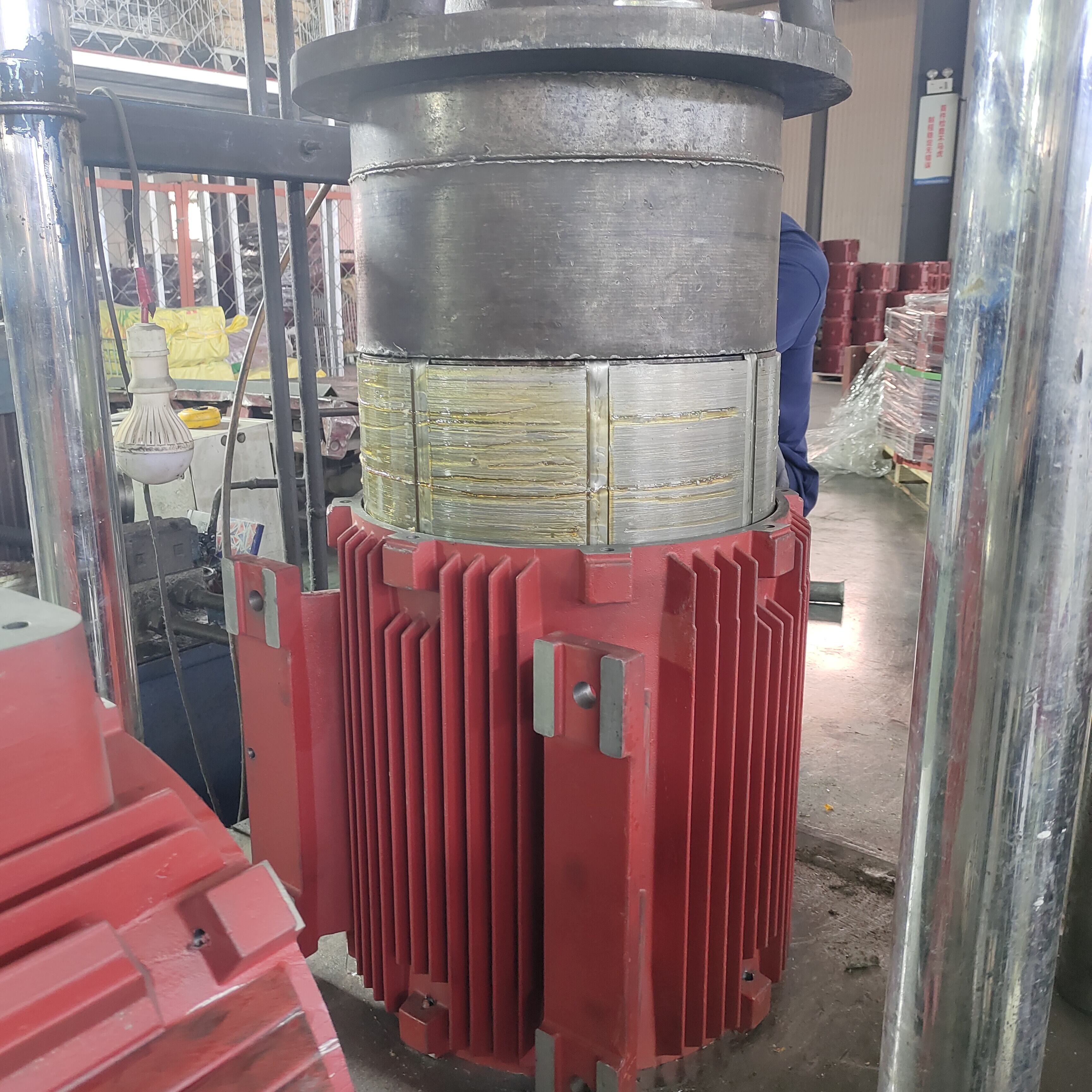
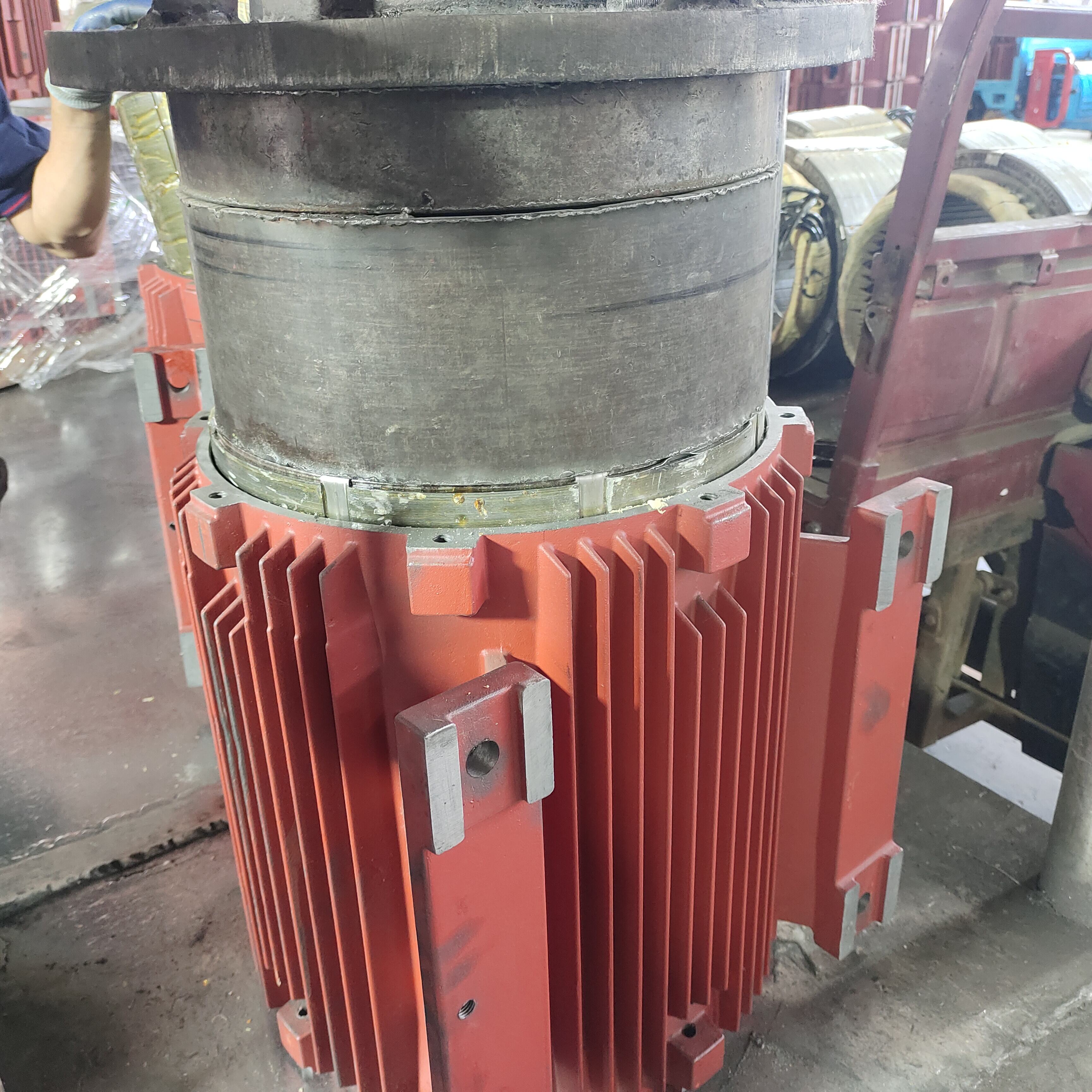
Warmtegietwerk verteenwoordig 'n revolusionêre vervaardigingsproses wat metaalproduksie transformeer deur die toepassing van beheerde hitte tydens die gietoperasie. Hierdie gevorderde tegniek behels die inspuiting van gesmelte metaal in presisie-ontwerpte staalgietvorms terwyl verhoogde temperature gedurende die hele produksiesiklus gehandhaaf word. Die warmtegietproses werk deur beide die gietvorm en die gesmelte metaal tot spesifieke temperatuurbereike te verhit, gewoonlik tussen 200 en 400 grade Celsius, afhangende van die metaallegering wat verwerk word. Hierdie temperatuurbeheer skep optimale omstandighede vir metaalvloei, verminder viskositeit en verseker volledige vul van die gietvormholte. Die hoofdoeleindes van warmtegietwerk sluit in die vervaardiging van komplekse geometriese komponente met uitstekende dimensionele akkuraatheid, die skep van onderdele met superieure oppervlakafwerking, en die vervaardiging van komponente wat minimale naverwerkingsoperasies benodig. Die tegnologiese eienskappe van hierdie proses sluit ingewikkelde temperatuurmonitorsisteme, outomatiese inspuitmeganismes en presisie-gietvormontwerpvermoëns in. Moderne warmtegiettoerusting sluit rekenaargecontroleerde verhittingselemente, gevorderde drukreguleringsisteme en real-time temperatuurterugvoerskringe in wat konsekwente verwerkingsomstandighede handhaaf. Die proses verrys in die vervaardiging van dunwandkomponente, ingewikkelde interne deurgange en onderdele met komplekse ondersnydinge wat uitdagend of onmoontlik sou wees om deur konvensionele gietmetodes te bereik. Toepassings vir warmtegietwerk strek oor verskeie nywerhede, insluitend motorvervaardiging vir motordelers en oordragonderdele, die lugvaartsektor vir liggewig strukturele elemente, die elektronikaindustrie vir hitteafvoere en behuisingkomponente, mediese toestelproduksie vir chirurgiese instrumente, en verbruikersgoedere-vervaardiging vir dekoratiewe en funksionele hardeware. Die veelsydigheid van warmtegietwerk maak dit geskik vir die verwerking van verskeie metaallegerings, insluitend aluminium, magnesium, sink en gespesialiseerde kopergebaseerde materiale, elk met spesifieke temperatuurprofiele en verwerkingsparameters wat nodig is om optimale resultate te verkry.