Intelligent Control Systems Optimize Performance and Safety
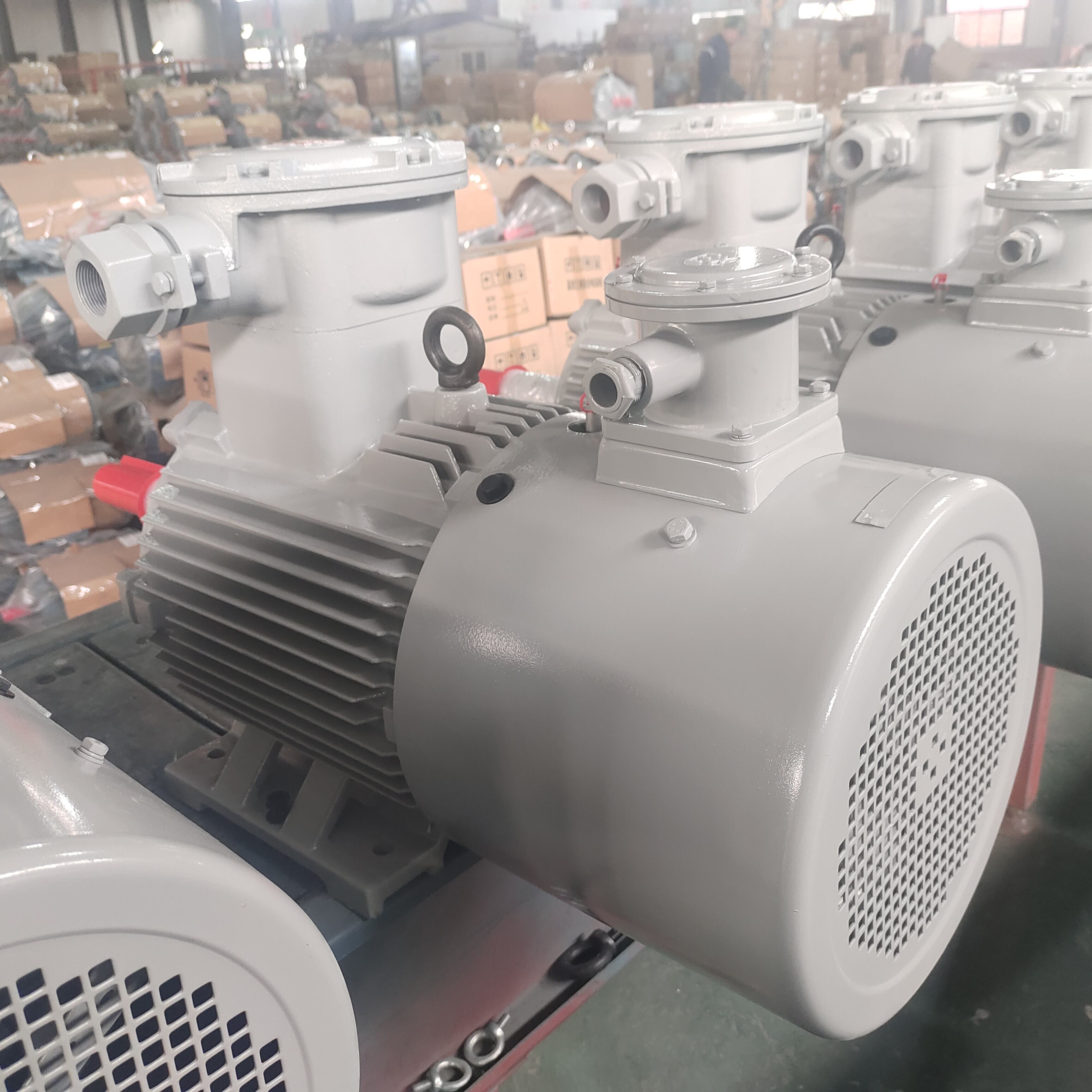
The popular wind turbine features sophisticated intelligent control systems that leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to maximize energy production while ensuring safe, reliable operations under all environmental conditions. These advanced control platforms continuously analyze thousands of data points per second, including wind speed measurements, direction changes, temperature fluctuations, vibration levels, and electrical output parameters to make real-time operational adjustments. The popular wind turbine control system employs predictive algorithms that anticipate wind pattern changes based on meteorological data and historical performance records, enabling proactive adjustments that maintain optimal energy capture efficiency. Automated safety protocols within the popular wind turbine immediately respond to potentially dangerous conditions, including extreme wind speeds, electrical grid disturbances, mechanical anomalies, or maintenance personnel proximity, triggering appropriate protective measures. Remote monitoring capabilities allow operators to supervise multiple popular wind turbine installations from centralized control facilities, reducing operational costs while improving response times to performance issues or maintenance requirements. The popular wind turbine control system integrates seamlessly with smart grid technologies, providing frequency regulation services, voltage support, and demand response capabilities that enhance overall electrical system stability and reliability. Condition monitoring systems within the popular wind turbine continuously assess component health through vibration analysis, oil quality testing, temperature monitoring, and acoustic signature evaluation, enabling predictive maintenance scheduling that prevents unexpected failures. User-friendly interface designs make the popular wind turbine control systems accessible to operators with varying technical backgrounds, featuring intuitive dashboards, comprehensive reporting tools, and customizable alert mechanisms. Cybersecurity measures protect the popular wind turbine control networks from potential threats through encrypted communications, secure authentication protocols, and isolated network architectures that prevent unauthorized access to critical operational systems.